Older people, professional athletes, and those whose work involves a long still session or standing on their feet are often exposed to various diseases of the musculoskeletal system. An irrational daily menu, physical inactivity leads to wear and tear, destruction of bone and cartilage material. As a result, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine develops, the symptoms and treatment of which depend on the personal characteristics of the body and the severity of the lesion.
According to the International Classification of Diseases of the 10th Revision, this disease was given the code M42. Sometimes patients get a cumbersome diagnosis, coding simplifies the work of doctors. This short alphanumeric name can be recorded in the medical history on the outpatient card. So what is lumbar spine osteochondrosis? What is the reason for its occurrence? What are the manifestations of the disease? This publication says it all.
Causes of lumbar osteochondrosis
Lumbar spine osteochondrosis often causes trauma and a slow-moving lifestyle. Among other things, one of the main roles is played by inherited inheritance, as well as the hormonal, chemical, psychogenic background of the body.
If parents have suffered from lumbar osteochondrosis, symptoms and treatment are likely to manifest and spread to their children. Once predisposing factors have been adopted through inheritance, offspring can also be at risk for this disease.
Provocators also include the following reasons:
- Other diseases such as digestive system, liver, pelvis, nervous system;
- Jump to a slower metabolism;
- Shift of acid-base balance towards oxidation (acidosis);
- Reduced engine energy;
- Stress, nervous situations;
- Long awkward posture, incorrect posture.
Sacral osteochondrosis often results from hypothermia, hormonal abnormalities, or abnormal congenital abnormalities of the spine.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
Signs of lumbar osteochondrosis are related to the fact that spinal nerve fibers pass through the posterior zone inside the spinal canal. The manifestations of the disease differ depending on the localization and the severity of the defeat of some roots.
The following symptoms appear in lumbar spine osteochondrosis:
- Pain Syndrome- Most patients complain of lower back pain in osteochondrosis. The pain radiates directly from the lesion to the local or gluteal region, the sacrum of the foot, in the zone of the lesion;
- Sign of tension- the pain increases by a certain position, but when the position of the body changes, the pain suddenly disappears. He got the most commonly used test from the explorer - Lasegue syndrome - and the pain intensifies when the straight limb is lifted and disappears when the foot bends to the knee;
- Decreased or increased sensitivity- this symptom is directly related to damage to the radical nerves, sensitivity is not disturbed at the site of the pathology, but at a certain distance. The patient suffers from hypoaesthesia, hypersesthesia, or paraesthesia caused by unusual projection sensations such as goose bumps, tingling, and so on. They characterize.
Often, in lumbar osteochondrosis, motor activity decreases, leading to varying degrees of muscle atrophy. In some circumstances, functions are limited, in other cases paralysis and paresis occur.
Lumbar chondrosis also involves damage to the blood vessels in the spine, with irritative and cramping vegetative changes. The blood circulation in the legs slows down, the lower limbs are constantly freezing, the skin is pale. Other organs in the lumbar region are often affected. Thus, with bladder damage, urinary incontinence develops or, on the contrary, is delayed.
Stages of Illness
- Grade 1 lumbar osteochondrosis is the initial type of pathology. It is characterized by a low density of intervertebral plates. Pain syndrome appears with a sharp turn of the body, after physical exertion or prolonged sitting.
This type of illness is common in drivers, office workers, athletes, and people working in harsh climates. Pain is not characterized by acute attacks, but develops in a debilitating dull or painful state.
At this stage, people are not in a hurry to see doctors, but are using traditional treatment methods such as ointments, compresses. The situation leads to the fact that lumbar or sacral spine osteochondrosis progresses to the second stage;
- Grade 2 lumbar osteochondrosis - degenerative and dystrophic disorders of the vertebral joints. The fibrous vertebral ring compresses as the nucleus pulposus grows and protrusion (protrusion) of the intervertebral disc occurs.
Neuropathologists define the second stage of osteochondrosis as lumbago. In other words, lumbago occurs in the lower back when a heavy object is suddenly lifted or with another load. This period lasts for many years, the stages of remission alternating with acute seizures of exacerbations;
- Grade 3 lumbar osteochondrosis - the protrusion of the pulp gradually increases, intervertebral hernia is formed. The patient develops a full range of neurological conditions: constant pain, buttocks, abdomen, tailbone, legs, urethral irradiation, restricted movement.
Legend is used to locate the hernia. A diagnosis of osteochondrosis L5 S1 means that the bulge of the nucleus pulposus occurred between the 5th lumbar and 1st vertebrae;
- If therapeutic measures are not taken in time, all stages of development flow smoothly into the next stage. Stage 4 of lumbar osteochondrosis is characterized by the development of complications.
In general, medication for severe pathology is not very effective. The neuropathologist is obliged to offer a radical method of action, i. e. hernia surgery.
Methods for diagnosing osteochondrosis
In order to identify the osteochondrosis of EPP, the neuropathologist first performs a history, as the patient's complaints are one of the determinants of an accurate diagnosis. During the conversation, the patient is asked questions about his or her health and condition - what and where it hurts, what the duration of the pain is, what enhances the feeling when stiffness appeared, whether treatment was performed, what it was and the like.
Definitely use instrumental diagnostic methods:
- General Rg-graphic image of the lumbar spine- the entire spine is taken or individual segments are photographed. Based on the complaints, a targeting Rg gram is made more often than others, in which the doctor perceives disc atrophy, decreased intervertebral space, appearance of osteophytes, smoothing of the lumbar bend;
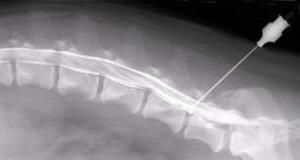
- Myelography- Contrast fluid is injected into the canal where the spinal cord passes through, with spinal tapping. The technique is used to determine the internal structure of the channel. Ordinary people find the procedure difficult to make and diagnose, but outside of contrast allergy, spinal canal is virtually non-threatening. Punching occurs at the site of the absence of the spinal cord;
- Computed tomography- compression of nerve roots, pulp protrusion determined, vertebral bodies, ligaments, blood vessels, soft tissues can be easily seen on the monitor;
Sacral osteochondrosis is most accurately determined using electromagnetic waves by examining the patient with a magnetic resonance imaging device.
Each tissue has its own incoming signal, the computer processes the data and displays the image on the screen. The doctor examines blood vessels, discs, bone processes, nerve fibers with a 1 mm cut. However, the patient does not get a harmful ionizing effect.
Treatment of lumbar spine osteochondrosis
Many patients are interested in the question: what to do with osteochondrosis of the lumbar region? Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine does not always have indications for surgery. The point is that after a thorough examination of the patient, the usual therapeutic measures will be sufficient.
Conservative therapy is declining:
- For medication;
- Physiotherapy procedures;
- Gymnastic exercises from gym therapy.
Manual therapy and traditional medicine are also used to treat lumbar spine osteochondrosis.
For the treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the surgical method is recommended for patients only in extremely severe cases, if the conservative methods did not give the desired result.
Medication
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is performed by a neuropathologist or the narrowest vertebrologist. Before treating lumbar chondrosis of spinous processes, the doctor determines the stage and severity of the abnormal disorders.
Muscle relaxants are used to relieve pain, cramps and inflammation. These medications quickly return to patient mobility, relieving cramps, so the pain goes away.
In addition to the group of muscle relaxants, steroid hormones are sometimes used to remove swelling and inflammation.
Physiotherapy
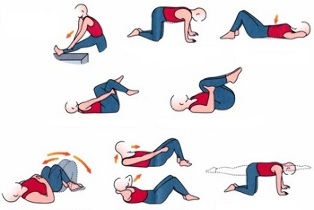
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis should be performed in conjunction with methods of exercise therapy. Exercise and exercise should be given the same attention as the use of medications.
The therapeutic effect of osteochondrosis is exercises that relieve pain, strengthen the muscle frame, reduce compression between the plates - this slows down the further progression of the disease.
Physiotherapy
For lumbosacral osteochondrosis, treatment involves the following procedures:
- Electrophoresis with drugs;
- Laser and magnetic therapy;
- Treatment with magnetic currents;
- Darsonval;
- UV irradiation;
- Diadine treatment;
- Shock wave method.
Manipulations involve the use of devices that use natural physical force: currents, light radiation, vibration, and so on. The treatment schedule and the duration of the physiotherapy course are determined by the attending physician.
Manual therapy
When a patient asks a neurologist how to manually treat osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, he or she is usually advised by a qualified professional who touches not only the muscle tissue but also the vertebrae with his hands.
In lumbar chondrosis, this method normalizes blood and lymph circulation, eliminates muscle tone and deformity, and restores motor function. The chiropractor's hand reduces the cleanliness of the cramps, reduces back pain.
How is osteochondrosis of the lumbar region treated using manual techniques, and is it possible to fully recover in this way? Manual therapy is prescribed only if the degenerative processes have not disturbed the tissues of the spine, i. e. , no bone growth has developed. The need for procedures is determined by the physician after Rg diagnosis, CT, or MRI.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of lumbar chondrosis is indicated in certain indications when the pathology is characterized by the following changes in the spine:
- The spinal canal narrows, the intervertebral discs are compressed and destroyed;
- Cauda equina syndrome develops - the massive nerve bundle of the spinal cone is damaged, which innervates the pelvic region, the legs;
- Decreased sensitivity progresses, impaired ability of internal organs to function;
- There is a risk of paralysis.
The operation is performed according to emergency or planned signals. The goal of surgical treatment is to relieve pressure and improve the condition of the spine.
Traditional Medicine
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine by folk methods is best done in consultation with your doctor.
The People's Pharmacy offers a number of medicines to cure diseases:

- Herbs, essential oils, flower extracts, plant roots;
- Animal products such as snake or bee venom, badger, dog, sheep fat, boiled egg and more;
- Iodine, turpentine and alcohol are used for warming, irritating effects.
Like drugs, lower back chondrosis is treated by folk methods only in the early stages of the disease, while the symptoms only disappear but the pathological changes do not disappear. Among other things, such treatment often has side effects, which is why professional consultation is required before using any prescription for traditional medicine.
Dosage of any folk or medicine should be prescribed by your doctor.
Complications
Lumbar chondrosis can lead to unpleasant consequences in the last stage, including disability.
In the background of dystrophy and degenerative disorders, narrowing and narrowing of the spinal canal develops. Such changes result in a chronic type of compression that disrupts normal blood flow, root ischemia, or cauda equina syndrome.
In addition, diseases such as spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis sometimes develop - intervertebral discs age, lose their strength, and pull pain occurs due to the disturbed structure of the vertebral joints. Complications are most often related to the spine of the lower spine, where spine-like bone growths form.
In the third stage, intervertebral hernias develop as a complication of osteochondrosis, diseases of the urogenital system and other internal organs appear.
Preventive measures
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine is of no importance. The lower back has the most load, so you need to be especially careful with your back. It is worth remembering that regular gymnastics exercises are the key to a healthy spine.
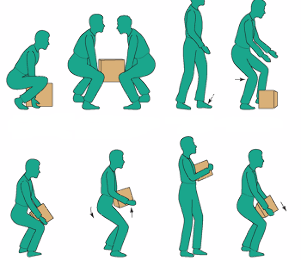
Weights should be lifted with the utmost care to avoid sudden jerks. Men and women can carry burdens that are within reason.
Sitting in the office, you should follow your posture, do the right posture, and sit on a chair with your back straight. It’s good to get up and walk around the room every hour, squat, flip the torso: it relieves tension in the entire locomotor frame.
Massaging trigger points is great. They are active or in latent form. Trigger points appear as a result of overload, strong stretching, repetitive work, bending, hypothermia, and other factors.
Knowing the causes of spasmodic areas, measures should be taken to prevent their formation. Recently, a trigger-point massager has become popular, it is better to use a special tool to prevent the appearance of painful foci than to treat them for a long and expensive time.























